Background Jobs
Background Jobs in Rails allow tasks to run asynchronously, outside the main request cycle, improving performance and user experience.
Table of Contents
What are Background Jobs in Ruby on Rails?
Background Jobs are tasks that run behind the scenes without blocking the user’s interaction with the application. Instead of performing time-consuming operations during a web request, Rails can enqueue jobs to run later in the background.
Common examples include sending emails, processing uploads, or calling external APIs.
Why are Background Jobs Useful?
Without background jobs, long-running tasks would:
-
Delay responses to users
-
Slow down the application
-
Make scaling harder
Background jobs help:
-
Keep web requests fast and responsive
-
Offload resource-intensive tasks to workers
-
Schedule tasks to run at specific times
-
Handle retries and failures efficiently
How Background Jobs Work?
Background jobs are usually defined as job classes (often with ActiveJob) and are processed by a queueing backend such as Sidekiq, Resque, or Delayed Job.
Key components:
-
Jobs: Ruby classes that define tasks to run in the background.
-
Queue adapters: Systems that manage and process queued jobs.
-
Workers: Processes that execute the jobs asynchronously.
-
Retry & error handling: Jobs can be retried automatically if they fail.
Example
Job (app/jobs/send_report_job.rb):
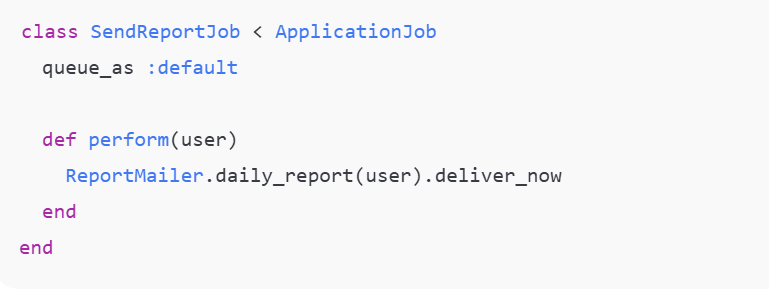
Defines a job to send a daily report email.
Enqueueing a job:

Queues the report job to run asynchronously in the background.
These examples show how background jobs let Rails handle time-consuming tasks without slowing down user requests.
Where to Use Background Jobs?
-
Sending emails or notifications
-
Processing file uploads or image transformations
-
Generating reports or analytics
-
Interacting with external APIs
-
Any task that doesn’t need to finish during a user request
In Summary
Background Jobs in Rails allow tasks to run asynchronously, keeping web requests fast and responsive. They improve performance, reliability, and scalability by offloading long-running operations to background workers.